Mechanical principle of the plunger pump
Overview The total stroke L of the reciprocating motion of the plunger pump plunger is constant and is determined by the lift of the cam. The amount of oil supplied per cycle of the plunger depends on the oil supply stroke, and the oil supply stroke is variable regardless of the camshaft control. The fuel supply start timing does not change with the change of the oil supply stroke. Turning the plunger changes the timing of the end of the oil supply, thus changing the amount of fuel supplied. When the plunger pump is working, under the action of the cam and the plunger spring on the camshaft of the fuel injection pump, the plunger is forced to reciprocate up and down, thereby completing the pumping task, and the pumping process can be divided into the following three stages. Oil feeding process When the convex portion of the cam is turned over, the plunger moves downward under the action of the spring force, and the upper space of the plunger (called the pump oil chamber) generates a vacuum degree, and when the upper end surface of the plunger puts the plunger into the sleeve After the oil hole is opened, the diesel oil filled in the oil passage of the oil pump enters the pump oil chamber through the oil hole, and the plunger moves to the bottom dead center, and the oil feed ends. Oil supply process When the camshaft turns to the convex portion of the cam to lift the roller body, the plunger spring is compressed, the plunger moves upward, the fuel is pressurized, and a part of the fuel flows back through the oil hole to the body oil chamber of the fuel injection pump. When the top surface of the plunger covers the upper edge of the oil inlet hole of the sleeve, the pumping chamber at the top of the plunger becomes a sealing oil chamber due to the small clearance of the plunger and the sleeve (0.0015-0.0025 mm). Continue to rise, the oil pressure in the pump oil chamber rises rapidly, the pump oil pressure> the oil valve spring force + the high pressure oil pipe residual pressure, push the oil valve out, the high pressure diesel oil enters the high pressure oil pipe through the oil discharge valve, sprays through the fuel injector Into the combustion chamber. Oil return process The plunger is supplied upwardly, and when the chute (stop supply side) which is ascended to the plunger communicates with the oil return hole on the sleeve, the low pressure oil passage of the pump oil chamber and the middle hole and the radial hole of the plunger head With the chute communication, the oil pressure suddenly drops, and the oil discharge valve is quickly closed under the action of the spring force to stop the oil supply. After that, the plunger is still going up. When the convex portion of the cam is turned over, the plunger is further lowered by the action of the spring. The next cycle begins. The plunger pump is based on the principle of a plunger. There is two check valves on one plunger pump, and the opposite direction is. When the plunger moves in one direction, a negative pressure occurs in the cylinder. At this time, a one-way valve opens the liquid and is sucked. In the cylinder, when the plunger moves in the other direction, the liquid is compressed and the other one-way valve is opened, and the liquid sucked into the cylinder is discharged. This mode of operation forms a continuous supply of oil after continuous movement.
Ball lenses Spherical ball lenses are commonly used for laser collimating and focusing, laser-to-fiber coupling, fiber-to-fiber coupling, and fiber-to-detector coupling. Larger spheres are easier to handle and ease the sensitivity of translational alignment. However, smaller spheres fit into smaller packages.
Sapphire and Ruby ball lenses are both made from Al203. Ruby or Ruby-Doped sapphire owes its red color to traces of chromium oxide (chromium content for ruby balls is typically >0.5%). While their physical and chemical properties are basically the same, their optical properties are somewhat different. Sapphire has superior optical transmission qualities. Ruby Balls are easier to see and therefore easier to handle for physical applications.
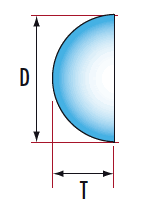
Ball Lens Half-Ball Lens
Specification of our ball lens: Sapphire Ball Lens,2 Mm Sapphire Ball Lens,Sapphire Half-Ball Lens,Sapphire Glass Ball Lens China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.csoptlens.com
*Material:BK7 or other optical glasses,optical crystal materials
*Diameter:1mm - 40mm
*Dimension Tolerance:+/-0.005mm
*Surface Quality:40-20
*Sphericity:0.005mm
*Coating:optional