Reasonable compounding of pesticides
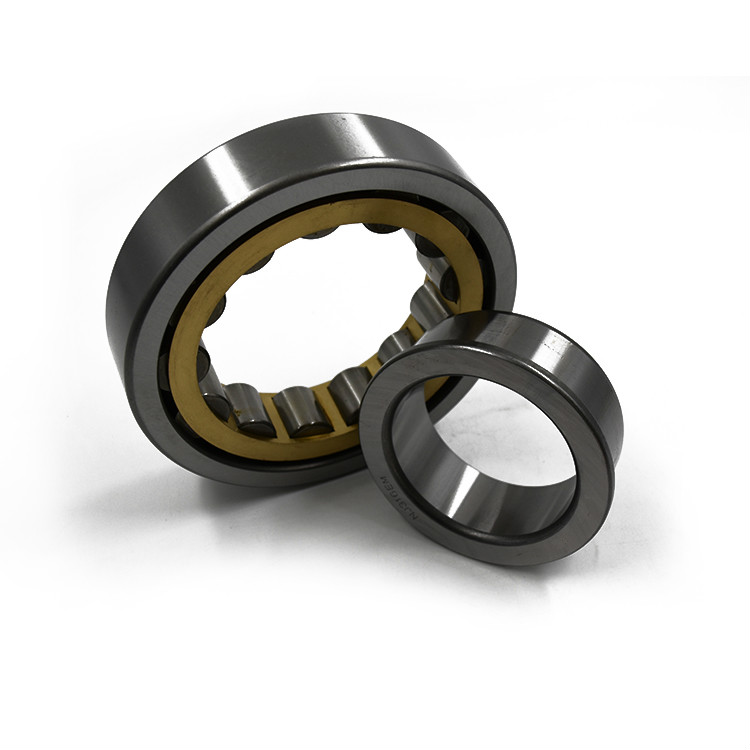
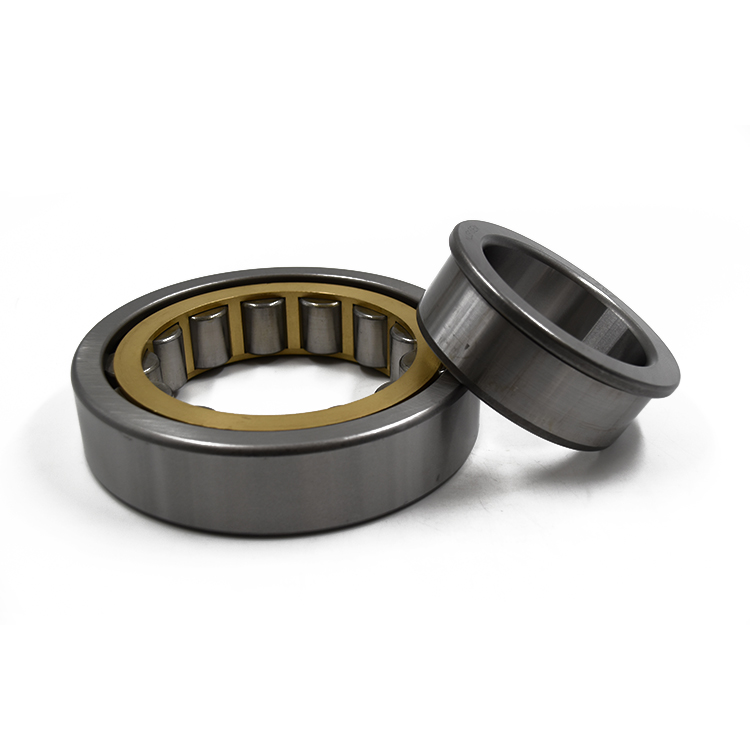
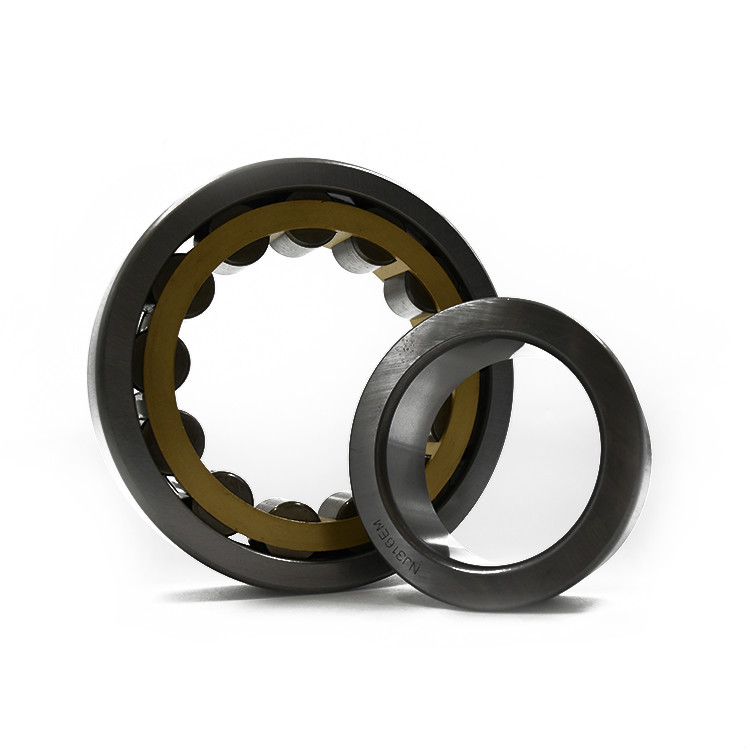
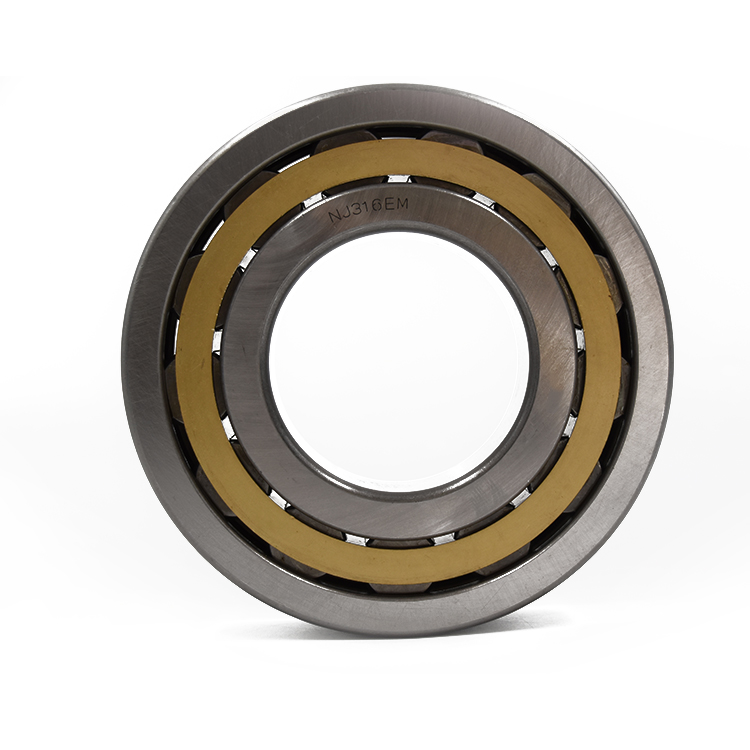
Cylindrical Roller Bearings are bearing in which cylinders are used as the rolling elements as opposed to balls in ball bearings. As such, the rollers have a greater (linear) contact area with the outer ring and are distribute loads across a broader surface. Subsequently, they have a relatively high radial load capacity and are suitable for high speeds. Double-row cylindrical roller bearings have high radial rigidity and are used primarily for precision machine tools.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings are designed to carry heavy radial loads. Our cylindrical roller bearings are made with a single row, two rows, or multi-rows of rolling elements to meet an application's radial load requirement. The radial Roller Bearing is available in many standard series and configurations, they are widely used in multiple industries. The combination of high load capacity, moderate speed rating, and industry interchangeability make it one of the most popular bearing designs. These cylindrical roller bearings are produced in ISO series metric, ABMA series metric and inch, journal type, Full Complement series, multi-row series, and cluster mill sizes. These bearings are dimensionally interchangeable to same numbered and sized bearings in the industry. Components of journal bearings and other standard series are made interchangeable with other manufacturer's components. Many mounting arrangements can be achieved with the multiple configurations available with the same load capacity for a given I.D., O.D., and width. Our cylindrical roller bearings can be manufactured in sizes from 3" bore diameter to 84" outside diameter. Internal radial clearances and cage designs can be engineered to your specific application when special applications are encountered.
Cylindrical Roller Bearing,Cylindrical Spherical Roller Bearing,Conveyor Cylindrical Bearing,Cylindrical Roller Ball Bearing Shijiazhuang Longshu Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.longsbearing.com
First, it should not affect the chemical stability of the active ingredients. The chemical nature and structure of the active ingredients of pesticides is the basis of their biological activity. When mixed, the active ingredient should not be chemically changed. One of the possible consequences of this chemical change is the decomposition of the active ingredient, which should be taken seriously.
Organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides are sensitive to alkali, and pyrethroid insecticides and dithioamino fungicides also decompose under more alkaline conditions. When acidic pesticides are mixed with alkaline pesticides, complex chemical changes occur and the active ingredients are destroyed. Some pesticide varieties are mixed and used under conditions where the alkalinity is not strong, and they cannot be placed for too long after compounding.
Second, the physical properties of the agent cannot be destroyed. The two types of emulsifiable concentrates are required to have good emulsifying, dispersing and moisturizing properties. When the two wettable powders are mixed, it is required to have good suspensibility, wettability and exhibiting properties. . This is not only a condition for exerting efficacy, but also prevents failure, physical reduction or phytotoxicity due to changes in physical properties.
Third, the price of pesticides should be reasonable. In addition to labor saving and time saving, the mixed use should generally be lower than the cost of single use. The same control object, generally high cost and low cost pesticides, as long as there is no resistance, often has obvious economic benefits. The more expensive new systemic fungicides are mixed with the less expensive protective fungicides; the more expensive pyrethroid pesticides are mixed with organophosphorus pesticides, which are less expensive than single use.
The fourth is to pay attention to the scope of use of compounding agents. It is necessary to clarify that there is a relationship between the scope of use of the pesticide after compounding and the scope of use of the single agent of various active ingredients contained therein. Mixed pesticides must have their own characteristics in the scope of use, so that the compounding is effective.