Talking about the Physical Properties and Application of Camel
Wen/Chen Tao Changzhou Fiber Inspection Institute Abstract: Camel velvet is a precious textile material. The physical properties of camel velvet, such as cross-section shape, length, fineness, curl, specific resistance and friction performance, are described in detail. The main products and uses of camel velvet are briefly introduced.
Elevator Components
& Elevator Spare Parts - Elevator Traveling Cable
Elevator Traveling Cable
Elevator traveling cable CAT6 CAT5e
Elevator Flat Cable
Elevator flat
traveling cable
Elevator Traveling
Cable Steel Core
Elevator Traveling
Cable with Supporting Steel Core
Elevator round
traveling cable
Elevator CCTV
cable
Elevator Traveling Cable CCTV
elevator control
cable
elevator flexible
cable
elevator screened
cable
elevator shielded
cable
elevator round
cable
elevator coaxial
cable
elevator section
cable
OTIS Elevator Traveling Cables, Thyssen Elevator Traveling Cables, KONE Elevator
Traveling Cables, GiantKONE Elevator Traveling Cables, ThyssenKrupp Elevator
Traveling Cables, Schindler Elevator Traveling Cables, XJ Schindler Elevator
Traveling Cables, Xizi OTIS Elevator Traveling Cables, Mitsubishi Elevator
Traveling Cables, Shanghai Mitsubishi Elevator Traveling Cables, Fujitec
Elevator Traveling Cables, Hitachi Elevator Traveling Cables, Toshiba Elevator
Traveling Cables, Hyundai Elevator Traveling Cables, LG Elevator Traveling
Cables, Sigma Elevator Traveling Cables, Express Elevator Traveling Cables,
GUANGRI Elevator Traveling Cables, FUJI Elevator Traveling Cables, BLT Elevator
Traveling Cables, CANNY Elevator Traveling Cables, SJEC Elevator Traveling
Cables, KOYO Elevator Traveling Cables, IFE Elevator Traveling Cables
Elevator Travelling Cable,Elevator Traveling Cable,Elevator Flat Cable,Elevator Flat Traveling Cable CEP Elevator Products ( China ) Co., Ltd. , https://www.zjsmartcommercialescalators.com
Key words: camel velvet; physical properties; application camelid family, Camelidae, ruminant livestock. It is a huge "magic" animal, and camel hair is an excellent textile material. The camels that are raised in China are mainly Bactrian camels, with a total of about 600,000 heads, accounting for about one-third of the world's total number of bactrian camels. The annual production of camel hair is about 2000t, which is the world's largest camel velvet producer. Production accounts for 20% of world production, ranking second in the world for camel cashmere.
1. Physical properties of camel velvet 1.1 Cross-section morphology The cross-section of camel velvet is generally circular, mainly composed of scaly and cortical layers of keratinous solid fibers, and a few containing medullary layers. The scales of camel velvet are close to the hair shaft, and the scales are less than wool or even cashmere, generally 40~60/mm, and the scales are thick, the stratum corneum of the scale surface is relatively smooth, the height of the rib base is low, and the scale angle of the scale is small. The fine fluff scales are mostly ring-shaped or oblique strips, so the camel fleece has the advantages of smooth surface, softness, small shrinkage, etc. The product is stable in size and smooth, just like the effect of resin finishing. The coarse hair is octagonal hollow, and the large black dots in the middle are hollow holes, and the small black spots scattered therein are the natural pigments contained. The scales are inlaid, the end faces are serrated, the visible shape of the protruding hair shafts is very irregular, and the bonding strength between the scales and the cortical cells is poor. These characteristics of camel velvet scales make it less velvety. The cortical cells of camel hairs are basically bilateral in structure, and the cortical cells are oblate, and the cortical cells are close to wool, but the intercellular substance is narrow. The rough and positive cortical cells are mostly sheath-core structures, so the rough hair is thick, hard, straight, straight and not curled. Most of the camelids (about 82%) are unmyelinated, but a few of the thicker velvets have punctiform pulp. In general, the velvet cavity of camel hair and hair is not developed. The fibers having a fineness of 50 μm or less are mostly punctate and elongated medulla. The chemical structure of camel hair and hair is very similar to that of sheep wool, and it is also composed of 18 kinds of amino acids.
1.2 Fiber fineness and length The difference in the fineness and length of camel velvet in different camel species and different regions, even in the same region, the fineness of camel velvet produced by the same camel species varies with age, gender, body parts, etc. . Among them, the camel velvet produced by the camel of 2~4 years old is thinner than that of the adult camel, and the female camel is thinner than the male camel. The fineness of camel hair is generally between 14 μm and 40 μm, and the average fineness is about 20 μm, which is equivalent to the thickness of 70 wool. The diameter of the coarse hair is generally above 50 μm, and the thickest is up to about 200 μm. There is also a certain amount of boundary hair between the rough hair and the fluff. This boundary hair often brings certain difficulties to the carding. Due to the harsh environment in which camels grow, the nutrition provided throughout the year is extremely uneven, so the fineness of different parts of the same fluff is quite different. Taking the fluff of adult camel as an example, the upper part of the velvet fiber is thicker, the middle part is second, the lower part is thinner, and the difference is larger, the less is 5μm~7μm, and the more is more than 10μm. The unevenness of the fineness of the single velvet fiber will affect the unevenness of other properties of the fiber, and thus the spinning performance. The length of camel hair is also different. The shortest is only 5mm, the longest is up to 115mm, the average length is about 60mm, the length of rough hair can reach 100mm~200mm, and the length of protective hair (bristles, elbows) can reach 200mm~ 500mm, of which the Alashan flag camel has a longer length and higher grade, and the spinning value is the best.
1.3 Curling The curl of camel hair is not as regular as wool. On the one hand, the bilateral structure of the cortical cells of camel hair is not as regular as wool, and the other is due to the unevenness of the fineness of camel fiber.
The curl of camel hair is generally deep and deep with a fineness of about 10 μm, reaching 6 to 7 crimps/10 mm, and its shape is mostly deep bend, narrow bend or loop bend. The camel velvet with a fineness of 20μm~30μm has fewer curls than the former, and its shape is mostly normal or shallow, and the number of curls is only 3~5/10mm. When the fineness is above 40 μm, there is substantially no curl, and only a small amount of irregular shallow or flat bends in the lower portion of the fiber, and the number of crimps is only 1 to 3/10 mm. The camel hairs are basically free of curl, and this part of the coarse hair is easier to remove during the combing. According to the measurement, the average number of curls of camel hair was 3.84/10 mm, the crimp ratio was 18.64%, the crimp modulus was 83.22%, and the residual crimp ratio was 15.51%. The degree of curl directly affects the cohesion between the fibers and the pilling performance of the product.
1.4 Friction performance The friction performance of camel velvet is the lowest among special animal fibers, because the number of scales of camel velvet is small, the scales and hair shafts are tightly cohesive and the scales are small.
The specific resistance value of 1.5 specific resistance camel hair is 1.003×1011 Ω·cm, which is larger than the specific resistance value of wool (3.66×108 Ω·cm). This is because the surface scale of camel velvet is uneven and the uneven state is strengthened. The agglomeration effect of static electricity makes it difficult for the charge to escape from the recess, and thus the antistatic property is poor. Therefore, in addition to the material should have a certain moisture regain in the processing process, it is necessary to add an appropriate amount of antistatic agent to the oiling agent in order to make the production go smoothly.
1.6 Mechanical properties The density of camel wool is 1.31 g/cm3~1.32g/cm3, the breaking strength is 5.89cN, the elongation at break is 41.62%, the elastic modulus is 231cN/tex, and the breaking length is 15.94km. Camel velvet has better compression performance than wool, and is not easy to shrink. The warming rate is 64.6%. It is often used as flakes to maintain its fluffy and warm performance in long-term use. The luster of camel velvet is comparable to that of rabbit fur, which is worse than cashmere, but better than yak velvet. The bending fatigue resistance is comparable to that of cashmere and is worse than rabbit hair. The performance of acid, alkali, oxidant and reducing agent of camel hair is strong. In cashmere, yak and wool. As far as its dyeability is concerned, since the fineness of the camel velvet is large, it is easy to dye, and an appropriate amount of leveling agent should be added during dyeing. At the same time, since the shrinkage rate of camel velvet in boiling water is high, The time of treatment during the dyeing process should not be too long. The above performance indicators are shown in Table 1. 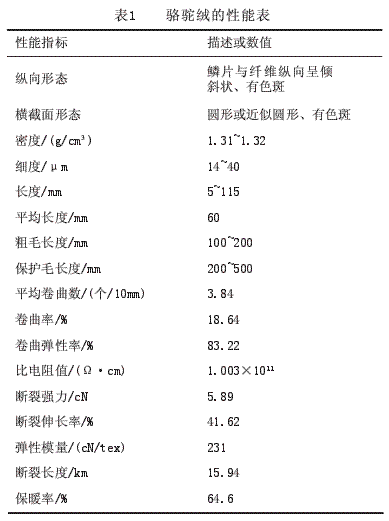
In addition, the moisture absorption of camel velvet is similar to that of wool: it absorbs quickly at the beginning, rises linearly, then gradually reaches equilibrium, but at the beginning absorbs moisture faster than wool.
2. The products and uses of camel velvet In the special animal fluff, except for mohair, the average length of camel velvet is longer, which can be adapted to wool spinning (worsted, roving) and cotton spinning processing systems, not only for pure spinning, but also with other The fiber raw material is blended. It can be made into combed strips like cashmere, worsted yarns can be spun on wool worsted and cotton spinning equipment, and woollen yarns can also be spun on woollen spinning equipment. When spinning spun yarns, ring, ingot or new spinning equipment can be used. It can be selected according to the mechanical properties of the non-wool and the use of the product.
Camel wool can be dyed dark or not dyed and used directly. When blended with other fibers, it can be dyed and then blended to maintain the same color. For blends with a large proportion or pure camel light color, it must be on camel. The velvet is decolorized. In general, the color of camel hair is not limited too much, and camel, light beige, rust red, navy, purple, brown, etc. can be produced. Camel velvet products are divided into knitted products and woven products. Among them, fine and woollen camel woven knitwear weft-knit camel velvet shirts are 100% pure camel velvet shirts, and there are also camel velvet and wool or blended shirts with other fibers. The camel velvet shirt has the characteristics of natural color, good elasticity and wear resistance, smooth hand feeling and good fluffiness. It is comfortable and elegant to wear. Usually, these sweaters are made of cotton yarn woven bottom, camel velvet yarn woven suede, and then woven and textured to form a thick, soft and elastic velvet product. The camel velvet is woven with trolleys, the camel velvet yarn is woven into a looped fleece, the camel velvet yarn is 133tex, the cotton yarn is interwoven with 29tex and 28tex, and the cashmere content is 50%. The flower camel velvet is woven with a jacquard circular machine, the velvet yarn is 133tex, the cotton yarn is 28tex, and the cashmere content is about 48%. The strip camel velvet and the wave camel velvet are warp knitted fabrics, which are generally made of 97tex pile yarn and 28tex, 29tex cotton yarn. The amount of cashmere is as high as 65%. In terms of woven products, a variety of products can be developed, such as short-sleeve coats (55% for camel velvet, 45% for wool or 30% for camel, 70% for wool), camel-women (30% for camel, wool) 70%), camel velvet flannel (Camel velvet 50%, wool 50%), smooth hair imitation copy coat (Camel velvet 50%, wool 50%), velvet coat (Camel velvet 30%, wool 70 % or warp with 100% wool, weft with 50% camel and 50% wool blend), women's floral coat (80% wool and 15% nylon blend for warp, 60% camel with weft) 40% wool blended yarn), camel velvet rug (70% for camel velvet, 30% for wool), camel velvet high velvet blanket (15% for camel velvet, 85% for wool), camel velvet blanket for both ends (Camel velvet 15 %, wool 85%), camel cashmere suede blanket (70% camel, 30% wool), can also be processed into plush, camel and cashmere or silk and other blended fabrics, everything, wool and cashmere can Made of products, camel velvet hair can do. The camel velvet fabric has natural luster, comfortable wearing, beautiful and elegant, strong and durable, moisture-absorbing and warm, and some properties also exceed wool products.
3. Summary Camel velvet is a precious and rare textile raw material. The development and utilization of camel velvet in China has just begun. The carding of raw velvet is still quite backward. There is no combing equipment suitable for camel velvet. The technical level of carding process remains to be determined. Further improve. At present, the extraction rate of camel velvet carding is less than 50%, and fiber damage is as high as 3%. At the same time, the improvement work of camel species is also relatively backward. The annual production and yield of each camel is not high. The only ones are 2.5~3.5kg, and the other ones can reach 12~16kg. How to improve the cashmere by improving the camel species? Gross production has great potential. In addition, the development of camel velvet products needs to develop in the direction of high mixing ratio, high grade and deep processing. Therefore, the development and application of camel velvet has broad prospects in China.
references:
[1] Xing Shengyuan, Jiang Xixia, Wen Yongfen, et al. Textile new materials and their identification [M] (1st edition). Beijing: China Textile Press, 2002.
[2] Xing Shengyuan, Wang Rui. Fiber Dictionary [M] (1st edition). Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007.
[3] Textile Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China. FZ/T 01057.3-2007 "Textile Fiber Identification Test Method Part 3: Microscopy" [S].

