Solar wafer without cutting strip technology
Abstract : Currently, crystal Rods used for solar wafer cutting are all glued with guide strips, but there are certain disadvantages in the use of guide strips. This article mainly discusses the non-guide strip cutting technology, which can not only ensure the cutting quality, but also achieve the purpose of cost reduction. 1 Introduction At present, crystal rods cut by a solar wafer cutting machine are bonded together by trays, glass, silicon blocks, and guide strips according to specific positions through epoxy resin, and the trays, glass, silicon blocks, and guide strips are surfaces. Horizontal, uniform thickness. The specific operation flow is as follows: (1) Prepare the tray and glass, clean it with a tray of paper and absolute ethanol, and tighten the tray Screws to check whether the glass frosted surface is even and smooth, and the side of the glass is crossed to facilitate positioning of the tray; (2) Epoxy glue is prepared, mixed according to proportion, smeared on the surface of the tray, and then the glass is bonded on the tray; (3) Prepare the silicon block, check the appearance quality of the silicon block, select the silicon block adhesive surface, and use alcohol and plates The paper wipes the bonding surface between the glass and the silicon block clean; (4) Prepare the epoxy resin glue, mix according to the proportion, smear on the glass surface, and bond the silicon block to the glass; (5) The glue will overflow to the silicon before curing. The residual glue on the surface of the block, glass and tray is cleaned; (6) Epoxy glue is prepared, and the guide strip is adhered to the surface of the silicon block, and each silicon block adheres to two guide strips. The purpose of the adhesive guide strip is as follows: due to the hard texture of the silicon block, when the steel is cut into the knife, the steel wire is in an unstable state after contacting the silicon block, and the steel wire fluctuates into the thick thin piece of the knife. Therefore, the guide bar is adhered to the surface of the silicon block. The guide strip is made of epoxy resin, quartz powder, catalyst, and fixative. It has good stability, no air bubbles, and is cured at room temperature. It is not easily deformed and is not easy to absorb water. Due to the soft texture of the guide strips, the steel wire will not generate large fluctuations after contacting the guide strips, which can effectively solve the problem of thick thin pieces of knife. 2 The drawbacks of using guide Bars During the process of cutting the crystal stick stuck with the guide strip, it is inevitable that some of the shredded guide strips will drop from the surface of the silicon block and fall into the cutting room of the machine tool. Possible bad results are: (1) When the guide strip is mixed into the mortar, the heat exchanger is easily blocked on the one hand, the flow rate of the mortar does not meet the requirements, the cutting quality is affected, and at the same time, the service life of the motor is shortened; on the other hand, the broken guide strip flows along with the mortar and is drawn into the line. The net will cause jumpers or crystal rods to be skewed, resulting in defective wafers such as thickness deviation films; (2) After the cutting is completed, after removing the crystal rod from the machine tool, the guide strip on the surface of the silicon block must be cleaned. If any residual guide strip is dropped into the middle of the silicon chip, the silicon chip can easily be washed during the cleaning process. broken; (3) During the cutting process, there will inevitably be a small amount of silicon falling onto the cutting room filter net. This part of the wafer must be cleaned for recycling. When the guide strip falls into the debris, it needs to be manually sorted out. Wasting a lot of manpower and time; (4) After cutting, the old mortar will be recycled through on-line recycling equipment. The principle is to separate the silicon carbide that meets the standard requirements in the old mortar after cutting by the centrifugal action of a centrifuge. The old mortar will have no cutting ability. The small particles are separated, a heavy liquid is obtained, and the heavy liquid can be used continuously. The light liquid produced by one centrifugation is subjected to secondary centrifugation, and the finely divided impurities are removed, and the reusable secondary light liquid is separated. However, when the mortar is mixed with broken guide strips, it will inevitably affect the quality of the recovered mortar, which in turn will lead to cutting quality problems. (5) Since the adhesive guide strips require the use of epoxy glue, a large amount of heat will be generated during the cutting process due to the friction between the silicon carbide and the silicon blocks to soften the rubber, so that when the steel wire passes through the adhesive layer of the blade surface At that time, the adhesive layer will scrape down the silicon carbide carried on the steel wire, and the steel wire will directly rub against the silicon block, which will easily lead to wire breakage. 3 No guide bar cutting technology The non-guide bar cutting technology mainly refers to that the surface of the silicon block no longer adheres to the guide bar. However, in order to avoid the problem of thin blade thickness, the cutting process of the tray tooling and the wire saw process used for bonding needs to be adjusted accordingly. The surface of the ordinary tray is a flat surface. The thickness of the two sides of the tray is the same. When using the non-guide strip technology, the surface of the tray needs to be ground into an inclined plane. The thickness of the two sides of the tray is inconsistent and is at an angle. The thickness deviation value on both sides of the tray is about 1.5 mm. . Take the HCT wire saw machine as an example. Figure 1 shows the side view of the inclined tray used by the guide wheel C and D. The tilt direction of the tray is the same (the tilt direction of the tilt tray used in the A and B wheels is opposite to the figure. ). According to the actual cutting situation, the entry side of the steel wire first passes through the side of the tray with a smaller thickness. In the following Fig. 1 as an example, when the No. 4 rod is being cut, the steel wire first passes through the right side as shown in Fig. 1, so that the steel wire is fixed in the silicon block after being cut into the silicon block, and is not easy to perform cutting. Cutting diagonally and adjusting the cutting process at the same time, it will no longer produce thick thin slices of knife into the knife, ensuring that the thickness of the cutting point is uniform. The wafers cut by the crystal rods with the guide bars bonded and the wafers with the crystal bars without the guide bars were randomly selected and tested for 10 samples. The thickness comparison conditions of the inserting points are as follows (unit: mm): From the above table, it can be seen that the non-guide strip cutting technology using tilted trays can ensure that the thinning of the knife can be avoided. The advantages of using non-guide strip cutting technology are: (1) No guide strips are mixed into the mortar to ensure the quality of the mortar. At the same time, the heat exchangers are not easy to be blocked and the service life is prolonged; (2) The guide strips are not included in the silicon wafers. To prevent the silicon wafer from being smashed, and no need to sort the guide strips from the broken silicon wafers, to avoid wasting a lot of time and manpower; (3) to reduce the production of plastic surface B4 and improve product quality. Due to the use of a sticky guide bar, the HCT machine tool is used as an example. Due to the presence of a wire bow on the exit surface of the No. 1 and No. 4 bars, the steel wire passes through the adhesive layer at the time of knife exit. At this time, the adhesive layer will grind off part of the mortar. As a result, the carrying capacity of the steel wire is reduced, cutting ability is reduced, and B4 chips are easily generated. When cutting with tilted trays, the steel wire passes through the silicon block first, and then passes through the adhesive layer, which can ensure the carrying capacity of the steel wire, and therefore can effectively reduce the production of the B4 film; (4) It can save the guide strips and sticks without bonding the guide strips. The cost of glue for the guide strips is reduced, and at the same time the number of steps for the bonding process is reduced, thereby reducing the amount of labor for employees and improving the work efficiency. 4 Conclusion The use of non-guide strip cutting technology can meet the requirements of the thickness of the cutting point of the silicon wafer cutting. At the same time, it has many advantages, which is of great significance to improve the quality of the silicon wafer. Flat Washer,aluminum Flat Washer,large flat washers,brass flat washers Jiangsu Minglu Stainless steel Co.,ltd , https://www.minglufastener.com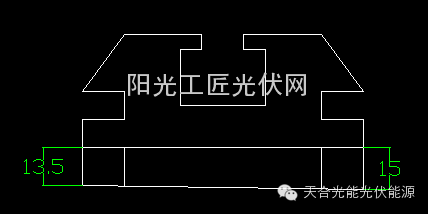
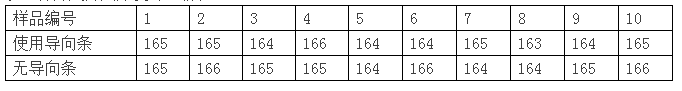
Table 1 Sample thickness comparison point