Laser cutting equipment (2)
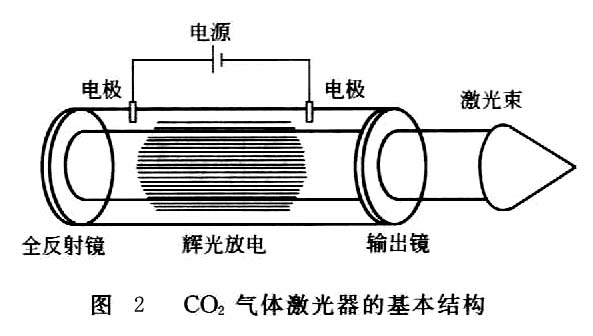
Table 2 Comparison of cutting performance of CO 2 laser and YAG laser project CO 2 laser YAG laser Focus performance The beam divergence angle is small, the basic mode is easy to obtain, the spot is small after focusing, and the power density is high. The beam divergence angle is small, and it is difficult to obtain single mode (only the ultrasonic Q-switched YAG laser can produce single mode), the spot is larger after focusing, and the power density is low. Metal absorption rate of laser (normal temperature) low high Cutting characteristics Good (large cutting thickness, fast cutting speed) Poor (low cutting capacity) Structural characteristics The structure is complex, the volume is small, and the precision of the optical path is high. Compact, small size, simple optical path and optical components Maintenance difference good Processing flexibility Poor (the transmission of the beam depends on the mirror and is difficult to transfer to different processing stations) Good (the optical fiber can be used to transmit the light beam, one laser can be used for multiple stations, and multiple identical lasers can be used) (1) CO 2 gas laser The CO 2 gas laser is a light amplification produced by using CO 2 gas (actually a mixture of CO 2 , N 2 and He) enclosed in a container as a working substance to undergo a shock oscillation. The basic structure of a CO 2 gas laser is shown in Figure 2. The gas is subjected to a glow discharge state by application of a high voltage, and a region between the mirrors is continuously excited by a mirror provided at both ends of the container to generate laser light. The CO 2 gas lasers are mainly of a gas-closed container type, a low-speed axial flow type, a high-speed axial flow type, and a cross flow type (that is, a discharge direction, an optical axis direction orthogonal to a gas flow direction). Laser cutting generally uses an axial flow CO 2 gas laser. The main characteristics of several CO 2 lasers are shown in Table 3. Previous Next